
Given an array nums. We define a running sum of an array as runningSum[i] = sum(nums[0]…nums[i]).
Return the running sum of nums.
숫자 배열을 줄테니, runningSum이라는 함수를 실행했을때 순서대로 숫자의 합이 담긴 배열을 리턴해라
# Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4]
Output: [1,3,6,10]
Explanation: Running sum is obtained as follows: [1, 1+2, 1+2+3, 1+2+3+4].
# Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,1,1,1,1]
Output: [1,2,3,4,5]
Explanation: Running sum is obtained as follows: [1, 1+1, 1+1+1, 1+1+1+1, 1+1+1+1+1].
# Example 3:
Input: nums = [3,1,2,10,1]
Output: [3,4,6,16,17]제약조건
- 1 <= nums.length <= 1000
- -10^6 <= nums[i] <= 10^6
나의 풀이
class Solution:
def runningSum(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:
sum = 0;
arr = [];
for idx, val in enumerate(nums):
for j in nums[:idx + 1]:
sum += j
print(idx, val, j)
arr.append(sum);
sum = 0;
return arr;이렇게 했더니 자꾸 Output Limit Exceeded 가 떠서 제약조건을 다시 확인하고, 테스트용 출력인 print문을 제거하였다.
class Solution:
def runningSum(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:
sum = 0;
arr = [];
if len(nums) > 1000:
nums = nums[:1000]
for idx, val in enumerate(nums):
for j in nums[:idx + 1]:
sum += j
arr.append(sum);
sum = 0;
return arr;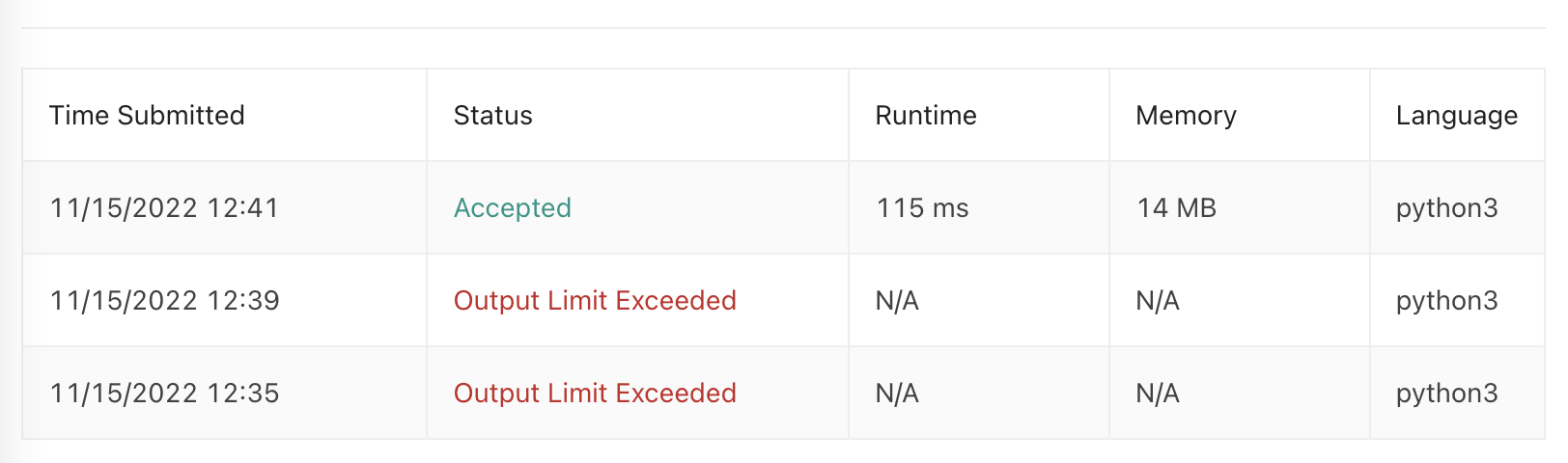
다른 사람의 풀이
class Solution:
def runningSum(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
nums[i] += nums[i - 1]
return nums
위와 같이 풀면 for문을 굳이 두번 쓸 필요가 없었다.
'💻 LEETCODE' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [LEETCODE] 876. Middle of The Linked List (0) | 2022.11.22 |
|---|---|
| [LEETCODE] 1342. Number of Steps to Reduce a Number to Zero (0) | 2022.11.16 |
| [LEETCODE] 412. Fizz Buzz (1) | 2022.11.15 |
| [LEETCODE] 1672. Richest Customer Wealth (0) | 2022.11.15 |
| [LEETCODE] 도망친 곳에 낙원은 없다. (0) | 2022.11.15 |




댓글